Time:2010-08-19
On Aug. 19, the Journal of Neuroscience published a research article from ION entitled "Nuclear Factor kappa B Controls Acetylcholine Receptor Clustering at the Neuromuscular Junction". This work was mainly carried out by Dr. Jia Wang and graduate student Xiu-Qing Fu, under the supervision of Dr. Zhen-Ge Luo.
The transcription factor nuclear factor_kappa B (NF-kB) is best known for its roles in inflammation and immune responses. However, its role in the nervous system remains unclear. Dr. Luo’s group investigated the function of NF-kB in the assembly of the postsynaptic apparatus at the vertebrate neuromuscular junction (NMJ). They found that upregulation of NF-kB promoted, whereas downregulation or inhibition of NF-kB attenuated, AChR clustering in cultured skeletal muscle cells. Mechanistic studies showed that RelA/p65 subunit of NF-kB is essential for the expression of Rapsyn, the scaffolding protein at the NMJ. In line with these findings, elimination of RelA/p65 in the skeletal muscle caused a decrease of AChR density at the NMJ. Thus, NF-kB signaling plays an important role in AChR clustering by transcriptional regulation of synaptic proteins, such as Rapsyn.
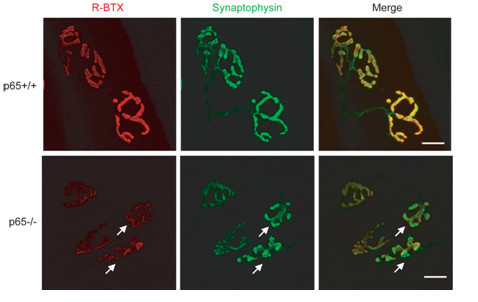
Aberrant AChR clustering in adult RelA/p65 mutant mice
 附件下载:
附件下载: